本帖最后由 POMIN 于 2023-8-21 11:17 编辑
用野火启明6M5开发板制作了一个基于 FreeRTOS 和 LVGL V8 的智能家居仪表盘,颜值较高,也可以作为桌面摆件使用,具体特点如下: - 采用 SPI + DTC 驱动 1.8寸 SPI 屏幕,超高帧率刷屏。
- 采用 LVGL V8 界面库绘制界面,有丰富控件、动画(FPS稳定50以上!)。
- 采用 ESP8266 联网,使用心知天气 API 获取当前天气并显示到屏幕。
- 采用 ESP8266 联网,通过 MQTT 协议连接到云服务器,上传状态数据。
- 采用鲁班猫2安装 EMQ 作为 MQTT 服务器,接收启明 6M5 上传数据。
- 采用 Node-RED + Homeassistant 接入家庭自动化,与智能家居设备完美联动。
硬件平台介绍野火启明 6M5 开发板使用野火启明 6M5 开发板来进行开发,开发板采用 R7FA6M5BH3CFC 作为主控芯片,有 2MB Flash,2MB!! 拿来开发 GUI 时的可发挥空间很大,接口有 SD 卡、以太网、PMOD、USB等等,接口很丰富,功能模块有 ESP8266、电容按键和实体按键等,功能十分的丰富。
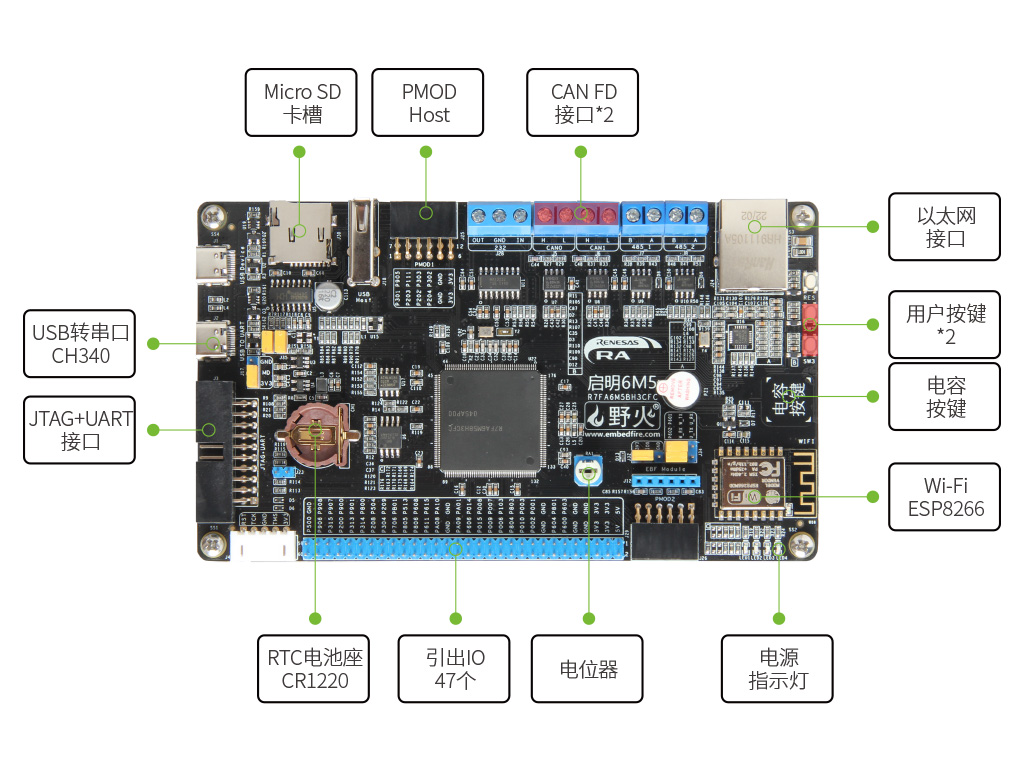 由于开发板板载的模块已经十分丰富,这里只外接了一个 SPI 屏幕和温湿度传感器模块 - 采用1.8寸的液晶显示屏,驱动芯片为ST7735S,SPI 接口。
- 温湿度传感器采用瑞萨的 HS3003 温湿度传感器,I2C 接口。
外设使用情况本次使用到了许多的外设,其中有如下外设 - 串口4 (SCI_UART4)作为调试串口使用
- 串口9 (SCI_UART9)连接到 ESP8266-AT 模块
- SDHI 连接到 SD 卡,提供文件系统的支持
- AGT 定时器为 LVGL 提供计时器
- RTC 提供实时的时间 (需要安装 CR1220 电池)
- SPI+DTC来实现屏幕的驱动,SPI 以最大速度 50MHz 运行
- TOUCH 提供电容按键
- I2C(SCI_I2C6) 连接到 HS3003 温湿度传感器
软件设计方案- 采用 FreeRTOS 作为本作品使用的RTOS
- 采用 LVGL V8 界面库来进行界面开发
- 采用 letter-shell 终端组件方便开发调试
- 采用 easylogger 日志组件方便调试
- 采用 cJSON 组件配合来完成网络数据包打包与解包
多线程由于代码较多,所以不作全面的介绍,只介绍几个线程的任务内容和软件包的使用,文末有开源链接,作品的代码全部开源,线程列表如下图,下面依次介绍 调试线程(debug_thread)该线程使用了 letter-shell 和 easylogger 软件包,提供完整的终端操作支持,同时支持日志打印,例如打印 esp8266 线程的调试日志。 使用自定义的命令来打印当前运行的任务列表 ESP8266 线程(esp8266_thread)该线程使用 AT 指令,实现开机自动连接 Wi-Fi、自动连接 MQTT 服务器、订阅主题。当收到消息队列的数据后,更新温湿度数据、LED状态,然后使用 cJSON 来打包为 JSON 数据包,发布到 MQTT 服务器的指定主题。当收到 MQTT 发来的数据后,使用 cJSON 来解析 JSON 数据包,更新当前天气等。 (触摸)按键、LED、RTC 线程(misc_thread)该线程使用了 MultiButton 软件包,可以实现一个按键的单击、双击、连击、长按等事件的处理,这里使用触摸按键来搭配这个软件包实现触摸按键控制板载的 LED 亮灭,并且发送状态信息到消息队列中,交由 ESP8266 线程上传到服务器端。 该线程同时也使用了 RTC 时钟,每秒触发一次中断,发送当前时间到消息队列中,交由 LCD 线程来显示当前时间。 SD 卡线程该线程使用了 Fatfs 来挂载文件系统,自动将 SD 卡挂载到 1: 分区下,提供给 LVGL FS 接口,实现 LVGL 加载 SD 卡中的文本、图片等文件。 屏幕驱动线程(lcd_thread)屏幕驱动使用硬件 SPI + DTC 的方案,这里没有使用 SCI 上的 SPI 接口,因为根据瑞萨 6M5 的文档得知挂在 SCI 上的 SPI 最大时钟频率为25Mhz,而直接连接的 SPI 最大时钟频率为 50Mhz,显然使用直连 SPI 接口可以获得更快的刷屏速度。 该线程会接收多个线程传入的消息队列:接收 RTC 时钟中断发来的消息队列,在 LVGL 中注册的 timer callback 函数中读取后显示到屏幕上,每秒刷新一次时间数据;接收温湿度线程发来的消息队列,读取后更新当前屏幕上的温湿度数值和进度条控件 温湿度传感器线程(sensor_thread)该线程每隔十秒使用硬件 I2C 来读取 HS3003 的数据并解算出温湿度数据,发送温湿度数据到消息队列中,交由 ESP8266 线程来上传到服务器和 LCD 线程来显示到屏幕。 LVGL 移植、界面设计LVGL 移植在本作品中对 LVGL 的显示接口和文件系统接口做了移植,下面对 LVGL 的显示接口移植做介绍,LVGL的显示接口只有三个函数需要修改,分别是缓冲区的初始化、屏幕的初始化和刷屏函数的接口,对于屏幕的初始化在 lcd_thread 中已经完成过,所以只需完成缓冲区的初始化和刷屏函数接口的适配。 为了实现更快的刷屏速度,使用官方提供的 example2 程序,并且给 LVGL 申请一个全屏缓冲区,搭配 SPI + DTC 的全屏缓冲区,需要更新屏幕上的数据时只需要搬运数据即可。
- #if 1
- /*********************
- * INCLUDES
- *********************/
- #include "lv_port_disp.h"
- #include <stdbool.h>
- /*********************
- * DEFINES
- *********************/
- #ifndef MY_DISP_HOR_RES
- #warning Please define or replace the macro MY_DISP_HOR_RES with the actual screen width, default value 320 is used for now.
- #define MY_DISP_HOR_RES 128
- #endif
- #ifndef MY_DISP_VER_RES
- #warning Please define or replace the macro MY_DISP_HOR_RES with the actual screen height, default value 240 is used for now.
- #define MY_DISP_VER_RES 160
- #endif
- /**********************
- * TYPEDEFS
- **********************/
- /**********************
- * STATIC PROTOTYPES
- **********************/
- static void disp_init(void);
- static void disp_flush(lv_disp_drv_t * disp_drv, const lv_area_t * area, lv_color_t * color_p);
- /**********************
- * STATIC VARIABLES
- **********************/
- /**********************
- * MACROS
- **********************/
- /**********************
- * GLOBAL FUNCTIONS
- **********************/
- void lv_port_disp_init(void)
- {
- /*-------------------------
- * Initialize your display
- * -----------------------*/
- disp_init();
- /*-----------------------------
- * Create a buffer for drawing
- *----------------------------*/
- /* Example for 2) */
- static lv_disp_draw_buf_t draw_buf_dsc_2;
- static lv_color_t buf_2_1[MY_DISP_HOR_RES * MY_DISP_VER_RES];
- lv_disp_draw_buf_init(&draw_buf_dsc_2, buf_2_1, NULL, MY_DISP_HOR_RES * MY_DISP_VER_RES); /*Initialize the display buffer*/
- /*-----------------------------------
- * Register the display in LVGL
- *----------------------------------*/
- static lv_disp_drv_t disp_drv; /*Descriptor of a display driver*/
- lv_disp_drv_init(&disp_drv); /*Basic initialization*/
- /*Set up the functions to access to your display*/
- /*Set the resolution of the display*/
- disp_drv.hor_res = MY_DISP_HOR_RES;
- disp_drv.ver_res = MY_DISP_VER_RES;
- /*Used to copy the buffer's content to the display*/
- disp_drv.flush_cb = disp_flush;
- /*Set a display buffer*/
- disp_drv.draw_buf = &draw_buf_dsc_2;
- /*Required for Example 3)*/
- //disp_drv.full_refresh = 1;
- /* Fill a memory array with a color if you have GPU.
- * Note that, in lv_conf.h you can enable GPUs that has built-in support in LVGL.
- * But if you have a different GPU you can use with this callback.*/
- //disp_drv.gpu_fill_cb = gpu_fill;
- /*Finally register the driver*/
- lv_disp_drv_register(&disp_drv);
- }
- /**********************
- * STATIC FUNCTIONS
- **********************/
- /*Initialize your display and the required peripherals.*/
- static void disp_init(void)
- {
- /*You code here*/
- }
- volatile bool disp_flush_enabled = true;
- /* Enable updating the screen (the flushing process) when disp_flush() is called by LVGL
- */
- void disp_enable_update(void)
- {
- disp_flush_enabled = true;
- }
- /* Disable updating the screen (the flushing process) when disp_flush() is called by LVGL
- */
- void disp_disable_update(void)
- {
- disp_flush_enabled = false;
- }
- /*Flush the content of the internal buffer the specific area on the display
- *You can use DMA or any hardware acceleration to do this operation in the background but
- *'lv_disp_flush_ready()' has to be called when finished.*/
- extern uint8_t lcd_buff[160][128][2];
- static void disp_flush(lv_disp_drv_t * disp_drv, const lv_area_t * area, lv_color_t * color_p)
- {
- if(disp_flush_enabled) {
- /*The most simple case (but also the slowest) to put all pixels to the screen one-by-one*/
- int32_t x;
- int32_t y;
- for(y = area->y1; y <= area->y2; y++) {
- for(x = area->x1; x <= area->x2; x++) {
- /*Put a pixel to the display. For example:*/
- /*put_px(x, y, *color_p)*/
- lcd_buff[y][x][0] = color_p->full >> 8;
- lcd_buff[y][x][1] = color_p->full;
- color_p++;
- }
- }
- }
- /*IMPORTANT!!!
- *Inform the graphics library that you are ready with the flushing*/
- lv_disp_flush_ready(disp_drv);
- }
- #else /*Enable this file at the top*/
- /*This dummy typedef exists purely to silence -Wpedantic.*/
- typedef int keep_pedantic_happy;
- #endif
对于刷屏函数的移植只需实现数据的搬运,代码如下。
- extern uint8_t lcd_buff[160][128][2];
- static void disp_flush(lv_disp_drv_t * disp_drv, const lv_area_t * area, lv_color_t * color_p)
- {
- if(disp_flush_enabled) {
- /*The most simple case (but also the slowest) to put all pixels to the screen one-by-one*/
- int32_t x;
- int32_t y;
- for(y = area->y1; y <= area->y2; y++) {
- for(x = area->x1; x <= area->x2; x++) {
- /*Put a pixel to the display. For example:*/
- /*put_px(x, y, *color_p)*/
- lcd_buff[y][x][0] = color_p->full >> 8;
- lcd_buff[y][x][1] = color_p->full;
- color_p++;
- }
- }
- }
- /*IMPORTANT!!!
- *Inform the graphics library that you are ready with the flushing*/
- lv_disp_flush_ready(disp_drv);
- }
在 lcd_thread 线程的 while 循环中只需使用 SPI 发送全屏缓冲到屏幕,代码如下
- void lcd_push_buff(void) {
- R_SPI_Write(spilcd_spi0.p_ctrl, lcd_buff, LCD_W * LCD_H * 2, SPI_BIT_WIDTH_8_BITS);
- }
- /* 下面是主函数调用 */
- void lcd_thread_entry(void* pvParameters) {
- FSP_PARAMETER_NOT_USED(pvParameters);
- lcd_setup();
- while (1) {
- lcd_push_buff();
- lv_task_handler();
- }
- }
界面设计与仿真采用 NXP 的 GUI Guider 作为 PC 端的设计器和仿真器,GUI Guider 可以在 PC 端完成一站式的 LVGL 界面设计与仿真,例如下图所示。 在 GUI Guider 中对两个页面分别创建了一个定时器,并且实现了两个回调函数,代码如下,通过这个定时器回调函数来实现周期性的刷新屏幕显示的内容,更新网络连接状态、当前温湿度、当前时间、当前天气等数据。
- void timer_main_reflash_cb(lv_timer_t *t)
- {
- static uint32_t tick;
- lv_ui * gui = t->user_data;
- #ifdef __ARMCC_VERSION
- float sensor_info[2];
- if (pdTRUE == xQueueReceive(g_sensor2lcd_queue, sensor_info, pdMS_TO_TICKS(0))) {
- lv_bar_set_value(gui->main_bar_humi, (uint32_t) sensor_info[0], LV_ANIM_ON);
- lv_bar_set_value(gui->main_bar_temp, (uint32_t) sensor_info[1], LV_ANIM_ON);
- lv_label_set_text_fmt(gui->main_label_humi, "%2d%%", (uint32_t) sensor_info[0]);
- lv_label_set_text_fmt(gui->main_label_temp, "%2d'C", (uint32_t) sensor_info[1]);
- }
- rtc_time_t get_time;
- if (pdTRUE == xQueueReceive(g_clock2lcd_queue, &get_time, pdMS_TO_TICKS(0))) {
- lv_label_set_text_fmt(gui->main_label_hour, "%02d", get_time.tm_hour);
- lv_label_set_text_fmt(gui->main_label_min, "%02d", get_time.tm_min);
- lv_label_set_text_fmt(gui->main_label_sec, "%02d", get_time.tm_sec);
- }
- uint32_t num = 0;
- if (pdTRUE == xQueueReceive(g_esp2lcd_queue, &num, pdMS_TO_TICKS(0))) {
- if (num > 38) {
- num = 99;
- }
- char path [30];
- sprintf(path, "1:1:lvgl/weather/%d.jpg", num);
- lv_img_set_src(gui->main_img_weather, path);
- }
- #endif
- }
- const char str_ch[][40] = {
- "连接WI-Fi...",
- "连接WI-Fi失败!",
- "连接WI-Fi成功!",
- "连接MQTT服务器...",
- "连接MQTT服务器失败",
- "订阅MQTT主题...",
- };
- void timer_loading_reflash_cb(lv_timer_t *t)
- {
- static uint32_t num = 0;
- lv_ui * gui = t->user_data;
- #ifdef __ARMCC_VERSION
- if (pdTRUE == xQueueReceive(g_esp2lcd_queue, &num, pdMS_TO_TICKS(0))) {
- lv_label_set_text(gui->loading_tip, str_ch[num]);
- lv_bar_set_value(gui->loading_process, num * 20, LV_ANIM_ON);
- if (num >= 5) {
- setup_scr_main(gui);
- lv_scr_load(gui->main);
- }
- }
- #else
- num += 3;
- lv_label_set_text(gui->loading_tip, str_ch[num / 20]);
- lv_bar_set_value(gui->loading_process, num, LV_ANIM_ON);
- if (num >= 100) {
- setup_scr_main(gui);
- lv_scr_load(gui->main);
- }
- #endif
- }
MQTT 与服务器解析使用 ESP8266 模块连接到 MQTT 服务器,因为 MQTT 也是自建的 EMQX 服务器,自由度相对 onenet 平台要大很多,这里的上传数据、下载数据都是统一由 MQTT 服务器搭配 node-red 来完成,避免来回地将 ESP8266 切换为透传模式来实现 HTTP 访问,全由服务器来进行数据的处理与打包,拖拽化开发自定义的 MQTT 消息处理流程不香吗? 例如上传当前温湿度、LED 状态、知心天气 API 获得当前的天气数据的流程设置如下 服务器端解析温湿度数据时,上传的数据包格式为 JSON 数据,形如 {“hum”:51.498504638671872,”tem”:30.258193969726564} 为了解析 MQTT 的数据包,需要编写一段代码来实现数据类型的限定,这里还加了保留到两位小数,其中的 “get humidity” 等函数只需编写如下一段 JavaScript 代码,经过解析后得到湿度数据,传入后面的 “is null ?” 节点后若不为空就更新数据给 Homeassistant 的设备。
- var field = msg.payload.hum;
- var out;
- if (field == null) {
- out = { payload: null };
- } else {
- if (typeof field === 'number') {
- if (Number(field) === Math.round(field)) {
- /* 整数 */
- out = { payload: field };
- } else {
- /* 小数 */
- out = { payload: field.toFixed(2) };
- }
- } else if (typeof field === 'boolean') {
- /* 布尔 */
- out = { payload: field };
- } else if (typeof field === 'string') {
- /* 字符串 */
- out = { payload: field };
- }
- }
- return out;
经过 HTTP 访问知心天气的 API 后,耶对得到的 JSON 结果进行解析,消息形如 - {
- "results": [
- {
- "location": {
- "id": "WTW3SJ5ZBJUY",
- "name": "Shanghai",
- "country": "CN",
- "path": "Shanghai,Shanghai,China",
- "timezone": "Asia/Shanghai",
- "timezone_offset": "+08:00"
- },
- "now": {
- "text": "Cloudy",
- "code": "4",
- "temperature": "35"
- },
- "last_update": "2023-08-13T12:10:14+08:00"
- }
- ]
- }
解析代码也非常简单,text 为当前的天气文本,code 为当前的天气代码 - var text = msg.payload.results[0].now.text;
- var code = msg.payload.results[0].now.code;
- return { payload: code };
然后发送最终的天气码到主题 /test/esp8266/sub,这个主题是 ESP8266 已经订阅的, ESP8266 线程完成数据的获取,然后发送天气码到消息队列,LCD 读取消息队列,得到天气码,然后读取 SD 卡中的天气图标,显示到屏幕上,完成天气图标的更新。 最终效果联网进度显示界面开机自动联网、进度条提示,FPS最低 50!这个瑞萨的 MCU 跑 LVGL 完全无压力 实时温湿度、时间数据显示接入Homeassistant 记录温湿度数据通过 node-red 接入到 HA 作为一个设备显示当前的温湿度数据和板载 LED 的状态 温度数据的历史曲线(开了空调温度是直线下降啊) 湿度数据的历史曲线 天猫精灵获取板载 LED 状态设置了单击触摸按键开关 LED2 亮灭的逻辑操作,然后会自动上传这个 LED2 的开关状态到 MQTT 服务器上,通过 node-red 来上传到 Homeassistent,搭配巴法云平台接入到语音助手,我用的是天猫精灵,可以通过语音助手获取到当前 LED2 的状态,当然只是做一个演示,可以实现的自动化智能家居当然还有很多的玩法。
总结- 本作品开发过程中体会到了瑞萨的开发软件十分的易用,方便,也学习到了 LVGL V8、MQTT 服务器数据包的收发,node-red 桥接 MQTT 消息包到 HA 的知识
- 完成以上所有的功能后 Flash 使用了 1 MB 出头(主要是 GUI 的资源文件),这个单片机是有 2MB 的Flash,界面开发还有很大的发挥空间。
- 1.8 寸的小屏比较小,可以换成更大的屏和增加触摸,但是 RA6M5 没有专门的屏幕驱动外设,如果要拓展成并口 MCU 屏或者 RGB屏还是有点受限的。
开源链接第三方软件包开源协议使用到了如下第三方软件包,除 FatFs 使用 BSD 外别的均为 MIT 开源协议 - CJSON
- EasyLogger
- FatFs
- letter-shell
- MultiButton
- LVGL V8
- FreeRTOS
开源代码链接
|